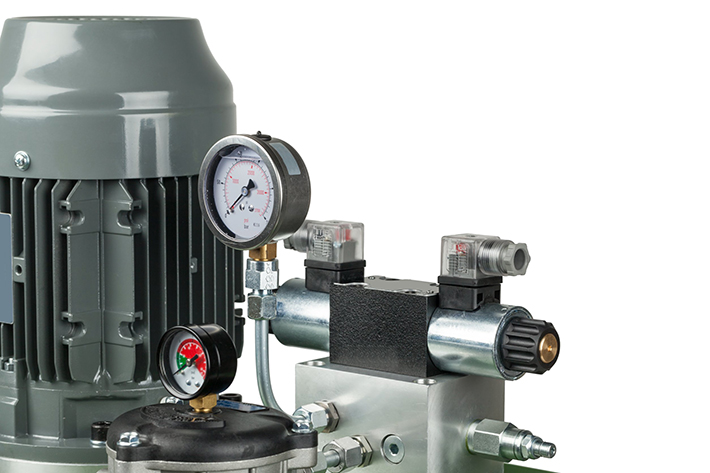
Hydraulic pumps play a crucial role in the manufacturing and construction industries. They are the workhorses that power countless machines, making them indispensable assets in modern operations. However, like any machinery, hydraulic pumps require proper care and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. In this article, you’ll learn about three best practices for operating these pumps.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance
It’s vital to regularly inspect and maintain your hydraulic pump. Just like an automobile needs periodic check-ups to keep it running smoothly, hydraulic pumps require routine attention to identify potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns. Inspect the pump’s exterior for any signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage. Check all connections, hoses, and fittings for tightness and integrity. Any loose connections or damaged components should be fixed promptly to prevent further damage.
Next, pay close attention to the pump’s fluid level and quality. Hydraulic systems rely on hydraulic fluid to transmit power efficiently. Contaminated or insufficient fluid can impair the pump’s performance and lead to premature wear and tear. Regularly monitor fluid levels and ensure that the fluid is clean and free from contaminants such as dirt, water, or air bubbles. If necessary, replace the hydraulic fluid according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
In addition to external inspections, it’s essential to perform periodic internal inspections of the pump’s components. This may involve disassembling the pump to inspect internal parts such as pistons, valves, and seals for wear or damage.
- Proper Fluid Selection and Contamination Control
The type and quality of hydraulic fluid used in a hydraulic pump can significantly impact its performance and longevity. Therefore, it’s crucial to select the appropriate hydraulic fluid based on the pump’s specifications and operating conditions. Using the wrong type of fluid or mixing incompatible fluids can lead to decreased efficiency, increased wear, and potential system failure.
When selecting hydraulic fluid, consider factors such as viscosity, temperature range, and compatibility with system materials. Consult the pump’s manual or manufacturer guidelines to ensure you’re using the recommended fluid for optimal performance. Additionally, be mindful of maintaining cleanliness and controlling contamination within the hydraulic system.
Contaminants such as dirt, moisture, and air can compromise the integrity of the hydraulic fluid and damage pump components. Implement effective contamination control measures, such as regularly changing filters, sealing hydraulic reservoirs, and minimizing exposure to external contaminants. This way, you’ll prolong the life of your hydraulic pump and keep it operating optimally.
- Proper Operating Procedures and Safety Measures
Operating hydraulic pumps requires adherence to proper procedures and safety measures to prevent accidents, injuries, and equipment damage. Familiarize yourself with the pump’s operating manual and follow the recommended guidelines for startup, shutdown, and operation. Avoid operating the pump beyond its rated capacity or under extreme conditions that could cause overheating or mechanical stress.
Ensure that all operators are trained and competent in the safe operation of hydraulic equipment. Provide proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and hearing protection, to mitigate hazards. Always follow lockout/tag out procedures when servicing or performing maintenance on hydraulic pumps to prevent accidental startup or release of stored energy.
Also, maintain safety devices such as pressure relief valves, safety guards, and emergency stop buttons to ensure they are functional and accessible. Implementing a comprehensive safety program that includes regular training, hazard assessments, and incident reporting will also promote a culture of safety and accountability in your workplace.
The Bottom Line
Operating hydraulic pumps efficiently and effectively requires adherence to best practices that prioritize inspection, maintenance, proper fluid selection, safety, and performance optimization. Investing time and resources into proper maintenance and operation upfront can save you from costly repairs and downtime.